Table of Contents
- How to Configure InterVLAN Routing & SVI Interfaces on Your Network
- Understanding the Different Types of InterVLAN Routing & SVI Interfaces
- Troubleshooting Common Issues with Configuring InterVLAN Routing & SVI Interfaces
- Best Practices for Setting Up InterVLAN Routing & SVI Interfaces
Configuring InterVLAN routing & SVI interfaces is a process of connecting multiple Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) with each other, as well as connecting them to the outside world. This is accomplished by creating VLANs on a Layer 2 switch and then configuring VLAN interfaces (also known as SVI interfaces) on the switch, which provides a routing interface between VLANs. This enables traffic to flow between VLANs, allowing devices on different VLANs to communicate with each other.
Exploring the Benefits of Configuring InterVLAN Routing & SVI Interfaces
InterVLAN routing and SVI interfaces are two of the most commonly used network configurations for larger companies. They offer a number of benefits that can enhance the performance and security of a company's network. In this article, we will explore the benefits of configuring InterVLAN routing and SVI interfaces. The first benefit of configuring InterVLAN routing and SVI interfaces is increased network performance. By using the SVI interfaces, it is possible to segment the network into multiple virtual LANs, which can help to reduce traffic congestion and improve network speeds.
Additionally, the SVI interfaces allow for multiple VLANs to be connected to the same physical router, which allows for more efficient routing of traffic and reduces the need for multiple physical routers. The second benefit of configuring InterVLAN routing and SVI interfaces is increased security. By segmenting the network into multiple VLANs, it is possible to better control access to sensitive resources. This makes it easier to prevent unauthorized access, as well as to quickly identify and respond to suspicious activity. The third benefit of configuring InterVLAN routing and SVI interfaces is greater scalability.
With the SVI interfaces, it is possible to easily add or remove VLANs as needed. This makes it easier to accommodate changes in the network, such as an increase in the number of users or the addition of new services. Finally, configuring InterVLAN routing and SVI interfaces can help to reduce costs. By reducing the need for additional physical routers, it is possible to save money on hardware costs. Additionally, it is possible to reduce the amount of time spent on configuration and maintenance, which can help to reduce operational costs. Overall, configuring InterVLAN routing and SVI interfaces offers a number of benefits that can help to improve the performance and security of a company's network. By using these configurations, it is possible to increase network performance, improve security, and reduce costs.
How to Configure InterVLAN Routing & SVI Interfaces on Your Network
InterVLAN routing is the process of routing traffic between multiple VLANs on a single network. It is necessary for large networks that have multiple VLANs and need to communicate between them. To configure InterVLAN routing, you will need to set up a router on a stick, which is a router that is connected to a switch on one side and a router on the other. The switch will have multiple VLANs configured on it and the router will have a physical interface for each VLAN. The first step in configuring InterVLAN routing is to configure the switch. Each VLAN will need to be configured with its own unique ID. The ID is used to identify traffic that should be routed between the different VLANs. Once the VLANs are configured, you will need to enable trunking on the switch.
Trunking allows the switch to pass traffic between the different VLANs. Next, you will need to configure the router on a stick. The router will need to be configured with the same VLAN IDs as the switch. It will also need to be configured with the appropriate IP addresses for each VLAN. The router will then be connected to the switch with a trunk cable. This will allow the router to route traffic between the different VLANs. The last step in configuring InterVLAN routing is to configure the switch. You will need to configure the switch to forward traffic between the different VLANs.
This is done by setting up the switch to forward traffic to the appropriate router interface for each VLAN. Once this is done, you will be able to route traffic between the different VLANs using the router. In addition to configuring InterVLAN routing, you may also need to configure SVI (switched virtual interfaces) on your network. SVI interfaces are virtual interfaces that are configured on a switch and used to route traffic between VLANs.
To configure SVI interfaces, you will need to configure the switch with the appropriate IP addresses for each VLAN. The SVI interface will then be connected to the switch with a trunk cable. This will allow the switch to route traffic between the different VLANs. By following the steps outlined above, you can configure InterVLAN routing and SVI interfaces on your network. This will allow you to route traffic between different VLANs and provide better network performance and security.
Understanding the Different Types of InterVLAN Routing & SVI Interfaces
InterVLAN routing is an essential component of any modern network. It is used to route traffic between different Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) within an organization. Without InterVLAN routing, the VLANs would exist in isolation, unable to communicate with each other. There are two primary types of InterVLAN routing: router-on-a-stick and Switched Virtual Interface (SVI). Router-on-a-stick is a type of InterVLAN routing where a single router is used to route traffic between multiple VLANs.
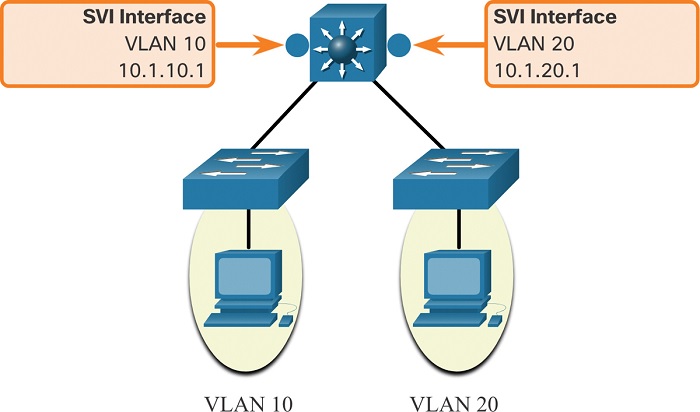
The router is connected to a single switch port that is configured with multiple 802.1q trunks. This trunk carries traffic from multiple VLANs and the router is able to route traffic between them. Switched Virtual Interfaces (SVI) are logical Layer 3 interfaces that are created on a switch. These interfaces are used to route traffic between different VLANs. Each SVI is created on the switch and configured to route traffic between the VLANs.
Both router-on-a-stick and SVI InterVLAN routing have their advantages and disadvantages. Router-on-a-stick is easy to configure but it requires a dedicated physical port on the switch. SVI is more complex to configure but it does not require a dedicated port on the switch. When deciding which type of InterVLAN routing to use, it is important to consider the size and complexity of the network, the resources available, and the desired outcomes. Both router-on-a-stick and SVI are useful tools for routing traffic between VLANs and can be used in the right circumstances to achieve the desired network performance.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Configuring InterVLAN Routing & SVI Interfaces
InterVLAN routing and SVI interfaces are essential tools for managing traffic between different VLANs in a network. However, these features can be difficult to configure and manage due to their complexity. In this article, we will discuss some common issues encountered when configuring InterVLAN routing and SVI interfaces, as well as best practices for troubleshooting them.
- The first issue that often arises is a misconfigured VLAN. If the VLANs are configured incorrectly, the traffic will not be routed correctly and the SVI interfaces will not be able to communicate with each other. To resolve this issue, it is important to carefully review the VLAN configuration and ensure that they are configured correctly.
- The second issue that can occur is a misconfigured router or switch. If the router or switch is not configured correctly, it may not be able to route traffic between the different VLANs. To resolve this issue, it is important to review the router or switch configuration and ensure that it is configured correctly.
- The third issue that may arise is a misconfigured IP address. If the IP address is not configured correctly, the SVI interfaces will not be able to communicate with each other. To resolve this issue, it is important to review the IP address configuration and ensure that it is configured correctly.
- The fourth issue that may arise is a misconfigured access list. If the access list is not configured correctly, the traffic between the VLANs will not be routed correctly. To resolve this issue, it is important to review the access list configuration and ensure that it is configured correctly.
- Finally, the fifth issue that may arise is incorrect trunking. If the trunk ports are not configured correctly, the traffic between the VLANs will not be routed correctly.
To resolve this issue, it is important to review the trunk port configuration and ensure that it is configured correctly. To ensure successful configuration and management of InterVLAN routing and SVI interfaces, it is important to carefully review each of the components involved in the configuration and ensure that they are all configured correctly. Additionally, it is important to keep a close eye on the router or switch configuration and ensure that it is up to date and functioning properly. With careful attention to detail and regular maintenance, configuring and managing InterVLAN routing and SVI interfaces can be a straightforward and successful task.
Best Practices for Setting Up InterVLAN Routing & SVI Interfaces
InterVLAN routing is essential for allowing communication between different VLANs on an organization's network. By setting up InterVLAN routing, devices within different VLANs can communicate with each other, allowing for efficient sharing of data and resources between them. In order to properly set up InterVLAN routing and SVI interfaces, there are certain best practices that should be followed. The first step in setting up InterVLAN routing is to create the necessary VLANs.
This can be done by configuring the VLANs in the switch using the appropriate commands. In order to enable communication between the different VLANs, a router is needed. The router can be connected to the switch using a trunk port. Once the VLANs and router have been set up, the next step is to configure the router for InterVLAN routing. This is done by creating SVI interfaces, one for each VLAN. Each SVI interface should be assigned a unique IP address, which will be used by devices within the VLANs to communicate with each other. The SVI interfaces should also be enabled to allow communication between the VLANs.
The last step is to configure the switch for InterVLAN routing. This is done by configuring each VLAN with the appropriate IP address and the proper routing protocol. This will allow devices within each VLAN to communicate with each other as well as with devices in other VLANs. By following these best practices for setting up InterVLAN routing and SVI interfaces, organizations can ensure that communication between different VLANs is enabled, allowing for efficient sharing of data and resources between them.
Conclusion
Configuring InterVLAN routing and SVI Interfaces is a powerful way for businesses to increase their network's performance and security. It enables them to segment their network into separate virtual LANs, or VLANs, which improves network performance and scalability, while also increasing security. By using InterVLAN routing and SVI Interfaces, businesses can ensure that their network traffic is efficiently routed and segmented for maximum performance and security.
Comments (0)